England And Wales on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the
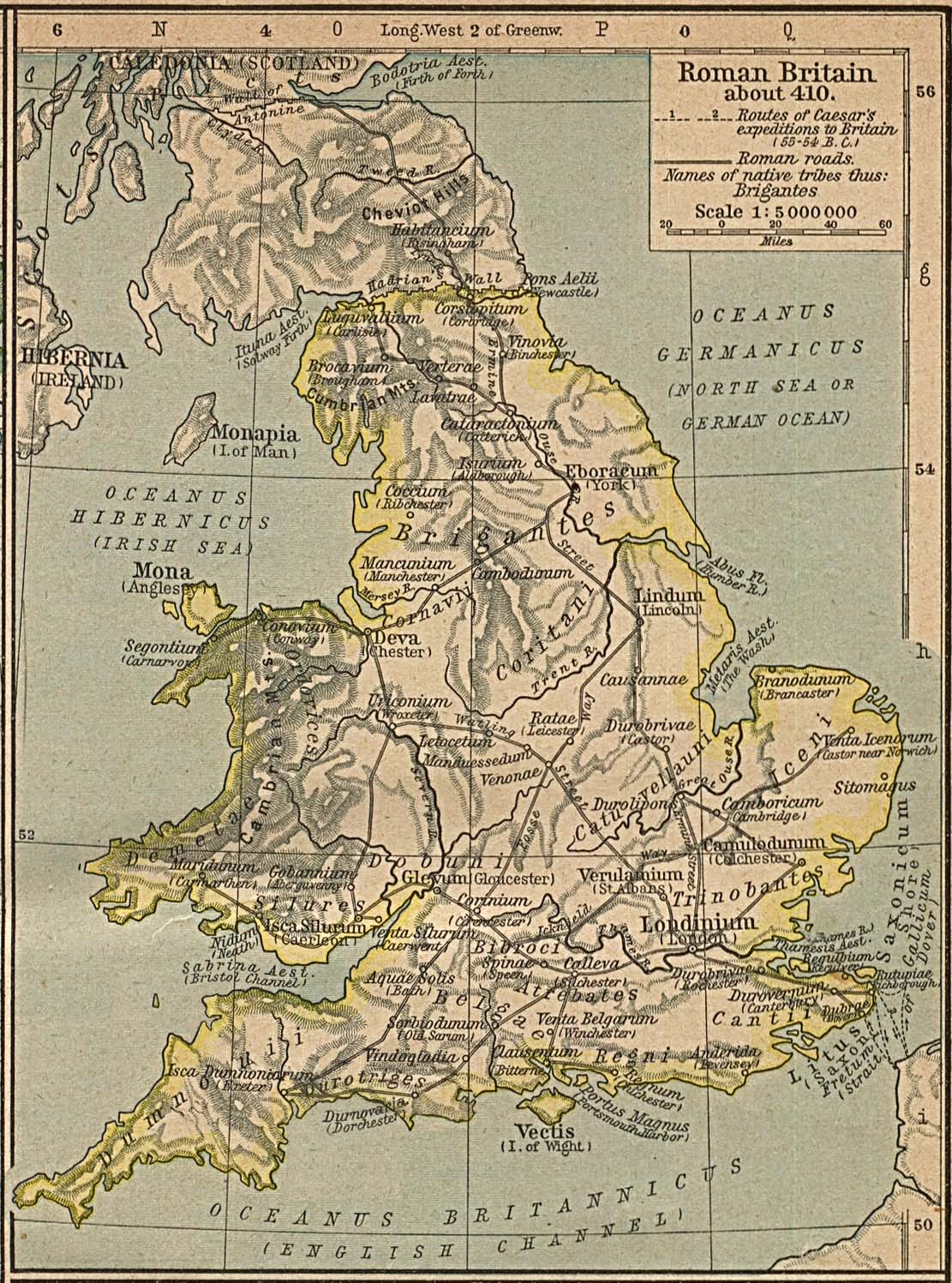 During the
During the
Graphicarchive of Graphic
Prior to 1746, it was not clear whether a reference to "England" in legislation included Wales, and so in 1746, Parliament passed the
 England and Wales are treated as a single unit for some purposes, because the two form the constitutional successor to the former Kingdom of England. The continuance of
England and Wales are treated as a single unit for some purposes, because the two form the constitutional successor to the former Kingdom of England. The continuance of
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. It covers the constituent countries England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is English law
English law is the common law list of national legal systems, legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly English criminal law, criminal law and Civil law (common law), civil law, each branch having its own Courts of England and Wales, ...
.
The devolved Senedd (Welsh Parliament; ) – previously named the National Assembly for Wales – was created in 1999 under the Government of Wales Act 1998
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
and provides a degree of self-government
Self-governance, self-government, self-sovereignty or self-rule is the ability of a person or group to exercise all necessary functions of regulation without intervention from an external authority. It may refer to personal conduct or to any ...
in Wales. The powers of the legislature were expanded by the Government of Wales Act 2006, which allows it to pass its own laws, and the Act also formally separated the Welsh Government
The Welsh Government ( ) is the Executive (government), executive arm of the Welsh devolution, devolved government of Wales. The government consists of Cabinet secretary, cabinet secretaries and Minister of State, ministers. It is led by the F ...
from the Senedd. There is currently no equivalent body for England, which is directly governed by the parliament and government of the United Kingdom
His Majesty's Government, abbreviated to HM Government or otherwise UK Government, is the central government, central executive authority of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland.
.
History of jurisdiction
 During the
During the Roman occupation of Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.
Julius Caesa ...
, the area of present-day England and Wales was administered as a single unit, except for the land to the north of Hadrian's Wall
Hadrian's Wall (, also known as the ''Roman Wall'', Picts' Wall, or ''Vallum Aelium'' in Latin) is a former defensive fortification of the Roman province of Roman Britain, Britannia, begun in AD 122 in the reign of the Emperor Hadrian. Ru ...
– though the Roman-occupied area varied in extent, and for a time extended to the Antonine/Severan Wall. At that time, most of the native inhabitants of Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the territory that became the Roman province of ''Britannia'' after the Roman conquest of Britain, consisting of a large part of the island of Great Britain. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410.
Julius Caes ...
spoke Brythonic languages, and were all regarded as Britons, divided into numerous tribes. After the conquest, the Romans administered this region as a single unit, the province
A province is an administrative division within a country or sovereign state, state. The term derives from the ancient Roman , which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire, Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
of Britain.
Long after the departure of the Romans, the Britons in what became Wales developed their own system of law, first codified by Hywel Dda (Hywel the Good; reigned 942–950) when he was king of most of present-day Wales (compare King of Wales); in England Anglo-Saxon law
Anglo-Saxon law (, later ; , ) was the legal system of Anglo-Saxon England from the 6th century until the Norman Conquest of 1066. It was a form of Germanic law based on unwritten custom known as folk-right and on written laws enacted by Histo ...
was initially codified by Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfr ...
in his Legal Code, . However, after the Norman invasion of Wales in the 11th century, English law
English law is the common law list of national legal systems, legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly English criminal law, criminal law and Civil law (common law), civil law, each branch having its own Courts of England and Wales, ...
came to apply in the parts of Wales conquered by the Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
(the Welsh Marches). In 1283, the English, led by Edward I, with the biggest army brought together in England since the 11th century, conquered the remainder of Wales, then organised as the Principality of Wales. This was then united with the English crown by the Statute of Rhuddlan of 1284. This aimed to replace Welsh criminal law with English law.
Welsh law continued to be used for civil cases until the annexation of Wales to England in the 16th century by the Welsh House of Tudor
The House of Tudor ( ) was an English and Welsh dynasty that held the throne of Kingdom of England, England from 1485 to 1603. They descended from the Tudors of Penmynydd, a Welsh noble family, and Catherine of Valois. The Tudor monarchs ruled ...
. The Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542 then consolidated the administration of all the Welsh territories and incorporated them fully into the legal system of the Kingdom of England. This was in part to update outdated Welsh laws, but also to control Wales alongside England; through these acts, the Welsh could be seen as equals to the English. This was reflected on both Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is known for his Wives of Henry VIII, six marriages and his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. ...
and Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
's coat of arms where the dragon represented Wales and the lion represented England. As soon as the Tudor dynasty ended with the death of Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. She was the last and longest reigning monarch of the House of Tudo ...
, however, the red dragon of Wales was dropped and replaced with the unicorn
The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since Classical antiquity, antiquity as a beast with a single large, pointed, spiraling horn (anatomy), horn projecting from its forehead.
In European literature and art, the unico ...
of Scotland with the succession of King James I who demoted Wales' status on the coat of arms and on the first adaptation of the Flag of Great Britain
The flag of Great Britain, often referred to as the King's Colour, first Union Flag, Union Jack, and Flag of the United Kingdom, British flag, was used at sea from 1606 and more generally from 1707 to 1801. It was the first flag of the Kingdom ...
. See alsGraphic
Wales and Berwick Act 1746
The Wales and Berwick Act 1746 (20 Geo. 2. c. 42) was an Act of Parliament, act of the Parliament of Great Britain that created a statutory definition of England as including England, Wales and Berwick-upon-Tweed.
The walled garrison town of Be ...
. This specified that in all prior and future laws, references to "England" would by default include Wales (and Berwick-upon-Tweed). The Wales and Berwick Act was repealed by the Welsh Language Act 1967, although the statutory definition of "England" created by that Act still applies for laws passed before 1967. In new legislation since then, what was referred to as "England" is now "England and Wales", while subsequent references to "England" and "Wales" refer to those political divisions.
Wales jurisdiction
There have been multiple calls from both Welsh academics and politicians for a Wales criminal justice system.Law
 England and Wales are treated as a single unit for some purposes, because the two form the constitutional successor to the former Kingdom of England. The continuance of
England and Wales are treated as a single unit for some purposes, because the two form the constitutional successor to the former Kingdom of England. The continuance of Scots law
Scots law () is the List of country legal systems, legal system of Scotland. It is a hybrid or mixed legal system containing Civil law (legal system), civil law and common law elements, that traces its roots to a number of different histori ...
was guaranteed under the 1706 Treaty of Union that led to the Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union refer to two acts of Parliament, one by the Parliament of Scotland in March 1707, followed shortly thereafter by an equivalent act of the Parliament of England. They put into effect the international Treaty of Union agree ...
, and as a consequence English lawand after 1801, Irish lawcontinued to be separate. Following the two Acts of Union, Parliament can restrict the effect of its laws to part of the realm, and generally the effect of laws, where restricted, was originally applied to one or more of the former kingdoms. Thus, most laws applicable to England also applied to Wales. However, Parliament now passes laws applicable to Wales and not to England (and vice versa), a practice which was rare before the middle of the 20th century. Examples are the Welsh Language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic languages, Celtic language of the Brittonic languages, Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales by about 18% of the population, by some in England, and in (the Welsh c ...
Acts 1967
Events January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Canadian Confederation, Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 6 – Vietnam War: United States Marine Corps and Army of ...
and 1993 and the Government of Wales Act 1998
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
. Measures and Acts of the Senedd apply in Wales, but not in England.
Following the Government of Wales Act, effective since May 2007, the Senedd can legislate on matters devolved to it. Following a referendum on 3 March 2011, the Senedd gained direct law-making powers, without the need to consult Westminster. This was the first time in almost 500 years that Wales had its own powers to legislate. Each piece of Welsh legislation is known as an Act of Senedd Cymru.
Company registration
For acompany
A company, abbreviated as co., is a Legal personality, legal entity representing an association of legal people, whether Natural person, natural, Juridical person, juridical or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members ...
to be incorporated in the United Kingdom, its application for registration with Companies House
Companies House is the executive agency of the British Government that maintains the Company register, register of companies, employs the company registrars and is responsible for Incorporation (business), incorporating all forms of Company, co ...
must state "whether the company's registered office is to be situated in England and Wales (or in Wales), in Scotland or in Northern Ireland",Subsection 9(2) of the Companies Act 2006 which will determine the law applicable to that business entity. A registered office must be specified as "in Wales" if the company wishes to use a name ending ''cyfyngedig'' or ''cyf'', rather than ''Limited'' or ''Ltd.'' or to avail itself of certain other privileges relating to the official use of the Welsh language.
Other bodies
Outside the legal system, the position is mixed. Some organisations combine as "England and Wales", others are separate. * In sports,cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
has a combined international team (simply called "England") administered by the England and Wales Cricket Board
The England and Wales Cricket Board, aka ECB, is the Sports governing body, national governing body of cricket in England and Wales. It was formed on 1 January 1997 as a single governing body to combine the roles formerly fulfilled by the Test ...
, who also govern the sport across both nations, and Glamorgan County Cricket Club participates in the English and Welsh county cricket system. In football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
, rugby union
Rugby union football, commonly known simply as rugby union in English-speaking countries and rugby 15/XV in non-English-speaking world, Anglophone Europe, or often just rugby, is a Contact sport#Terminology, close-contact team sport that orig ...
, rugby league
Rugby league football, commonly known as rugby league in English-speaking countries and rugby 13/XIII in non-Anglophone Europe, is a contact sport, full-contact sport played by two teams of thirteen players on a rectangular Rugby league playin ...
, the Commonwealth Games
The Commonwealth Games is a quadrennial international multi-sport event among athletes from the Commonwealth of Nations, which consists mostly, but not exclusively, of territories of the former British Empire. The event was first held in 1930 ...
and other sports have separate national representative teams for each country. A few Welsh association football clubs, most notably Cardiff City F.C. and Swansea City A.F.C., play in the English football league system, while The New Saints F.C., which represents places on both sides of the border, plays in the Welsh football league system. The Anglo-Welsh Cup was a rugby union competition contested by Welsh regions and English Premiership clubs between 1971 and 2018.
* Some religious denominations organise on the basis of England and Wales, most notably the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, but also small denominations, e.g. the Evangelical Presbyterian Church. Prior to the disestablishment of the Church in Wales
The Church in Wales () is an Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses.
The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishops. The position is currently held b ...
in 1920, the Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
church in Britain operated under the jurisdiction of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
throughout Wales and England.
* The Electoral Commission
An election commission is a body charged with overseeing the implementation of electioneering process of any country. The formal names of election commissions vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, and may be styled an electoral commission, a c ...
maintains a register of political parties, organised according to where the party operates (either ''England'', ''Wales'' or ''England and Wales''). The Green Party of England and Wales stands candidates only in English and Welsh constituencies; separate Green parties exist in Scotland and in Northern Ireland.
* Some professional bodies represent England and Wales, for example the Institute of Chartered Accountants in England and Wales, the General Council of the Bar, The Law Society, the National Farmers Union and the Police Federation of England and Wales.
* Other examples include the Canal & River Trust, the Charity Commission, the General Register Office for England and Wales, His Majesty's Inspectorate of Constabulary and Fire & Rescue Services, HM Land Registry, His Majesty's Prison Service
His Majesty's Prison Service (HMPS) is a part of HM Prison and Probation Service (formerly the National Offender Management Service), which is the part of His Majesty's Government charged with managing most of the prisons within England and ...
, Mountain Rescue England and Wales, the Worshipful Company of Chartered Accountants and the Youth Hostels Association.
Order of precedence
The order of precedence in England and Wales is distinct from those ofNorthern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ; ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, part of the United Kingdom in the north-east of the island of Ireland. It has been #Descriptions, variously described as a country, province or region. Northern Ireland shares Repub ...
and Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, and from Commonwealth realm
A Commonwealth realm is a sovereign state in the Commonwealth of Nations that has the same constitutional monarch and head of state as the other realms. The current monarch is King Charles III. Except for the United Kingdom, in each of the re ...
s.
National parks
Thenational park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
s of England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
and Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
have a distinctive legislative framework and history.
See also
* Courts of England and Wales * Cultural relationship between the Welsh and the English * Judiciary of England and Wales * Proposed Wales justice systemReferences
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:England And Wales